LIN simulation
Overview of LIN simulation engineering
With the continuous evolution of automotive E/E architecture and advancements in intelligence, in-vehicle networks have become more layered and diversified. In domains such as body control and comfort modules, where requirements for bandwidth and real-time performance are relatively lower, the LIN bus has gained widespread adoption due to its advantages of low cost and high reliability. The functional logic of various ECUs, especially LIN slave nodes like sensor and actuator controllers, and the interaction timing between master and slave nodes have become increasingly sophisticated, leading to a higher dependency on simulation testing. Utilizing tools like ETStudio to establish a LIN bus simulation environment can effectively emulate LIN network communication, master node scheduling, and slave node response behavior. This enables early verification of protocol compliance, functional logic correctness, and network management conformity during component development. Based on the simulation environment, developers can initiate integration testing earlier, accelerating the functional development and defect identification of their own products, thereby significantly improving development efficiency and product quality.
LIN simulation engineering plays a critical role in the development lifecycle of ECUs, particularly LIN slave node modules. It requires close collaboration with stages such as requirements analysis, low-level software configuration, application layer software development, integration testing, hardware-in-the-loop testing, and even after-sales diagnostics. For LIN nodes involving complex wake-up/sleep management, frame scheduling, or diagnostic services, a high-fidelity simulation environment can greatly reduce the complexity and cost of real-vehicle or real-hardware testing, shortening the development and verification cycle.
LIN Simulation Engineering Development Process and Strategy
In the early stages of LIN node module development, a thorough analysis of the LIN Description File (LDF), based on specific OEM LIN specifications and product requirements documents, is essential. Key aspects to clarify include the master node's schedule table, the signal publish/subscribe relationships of slave nodes, the arrangement of diagnostic frames, and network management strategies. The software testing team or a dedicated network simulation team is typically responsible for the initial setup and subsequent maintenance of the simulation project, ensuring the simulation model closely aligns with real network behavior.
LIN Simulation Engineering Development Strategy
Given the differences in LIN specifications among various OEMs and vehicle platforms, developers need to formulate targeted simulation strategies to meet specific project needs. The following are key considerations during the construction of a LIN simulation project, which contribute to building a high-quality simulation environment:
- Prioritize Official LDF Files: Whenever possible, use the LIN Description File (LDF) provided by the OEM to ensure absolute accuracy of parameters such as baud rate, frame IDs, signal definitions, and schedule tables, avoiding troubleshooting efforts caused by errors in self-built databases.
- Conduct In-Depth Requirements Analysis and Documentation: During the simulation preparation phase, clearly define the LIN frame types to be simulated (unconditional frames, event-triggered frames, sporadic frames, etc.), signal interaction logic, diagnostic services (e.g., reading data identifiers), and network management behaviors (wake-up/sleep). This lays a solid foundation for the architectural design of the simulation project.
- Actively Participate in Phase Reviews: Engage proactively in requirements reviews, LDF file reviews, test case reviews, etc. Brainstorming during these reviews helps avoid missing critical LIN communication requirements, misunderstanding scheduling logic, or having incomplete test scenario coverage.
- Timely Synchronization of LDF Changes: Closely track project progress to ensure timely access to the latest LDF file versions and adjust the frame structure, signals, or scheduling parameters within the simulation model accordingly.
- Plan for Physical Node Replacement: Once hardware samples are available, develop a plan to gradually replace simulated nodes with real ECUs for hardware-in-the-loop simulation, obtaining more accurate integration test results.
- Construct a Rational Simulation Project Structure: a. Modular Separation of Master and Slave Nodes: Design the LIN master node simulation and individual slave node simulations as independent modules. This allows flexible enabling/disabling during testing, facilitating fault isolation and test combination. b. Encapsulation of Common Logic: Encapsulate code with low correlation to specific node functions, such as LIN protocol handling (e.g., checksum calculation) and generic signal conversion, into reusable modules to reduce repetitive development. c. Reserve Expansion Interfaces: Provide configuration interfaces or data channels for potentially added LIN nodes or signals, enhancing the project's scalability.
- Implement Robust Version Management for Projects and Tools: Back up project configurations and perform compatibility tests before and after upgrades of simulation software like ETStudio to ensure project usability across different software versions.
- Enforce Strict Code and Documentation Management: Implement version control (e.g., Git) for the simulation project's source code, requiring commit records for any modifications. Upon project release, synchronously update version notes, configuration documents, and user guides.
LIN simulation engineering example
Implemented Functions
Taking a simple LIN network for window control as an example, the main simulation functions to be implemented include:
- Control Operation: Provide a simulation control panel to emulate driver operations on window switches (master node sending control commands), as well as sending LIN master node wake-up and sleep commands.
- Communication Simulation: Simulate the LIN master node periodically sending master frames containing control signals according to the schedule table defined in the LDF. Simulate the window motor controller (slave node) sending response frames containing status signals (e.g., position, stall) upon receiving valid frames.
- Logic Response and Display: The simulation model dynamically updates the window status (e.g., moving up, moving down, stopped, current position percentage) based on LIN message interaction and provides intuitive visualization on a graphical interface.
- Protocol and Data Analysis: Utilize the tool's message Timeline Trace window to monitor the frame sequence and signal values on the LIN bus in real-time. Use graphing windows to plot the variation of key signals (e.g., motor current, position feedback) over time for analyzing timing logic and performance.
Project realization
Added LIN bus support
Readers can add a Lin channel and modify the hardware properties to available hardware through the Device→Channel Assignment→Channel Config in the main menu. After adding, right-click on the Lin Network position in the system view on the right side of the Simulation Setup window to quickly add a network called LIN, and you can see an independent LIN network without any nodes on the network attempt.
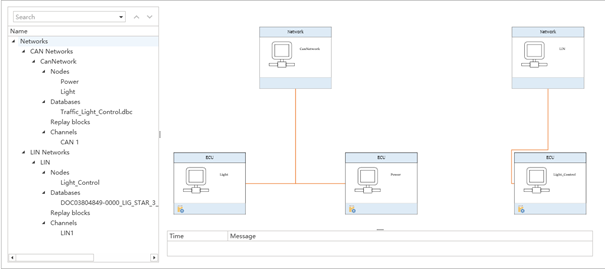
Database LDF file import
Similar to the CAN bus, the LIN bus also has database files for managing related messages and signals, so that ETStudio can quickly and clearly parse the data information on the LIN bus.
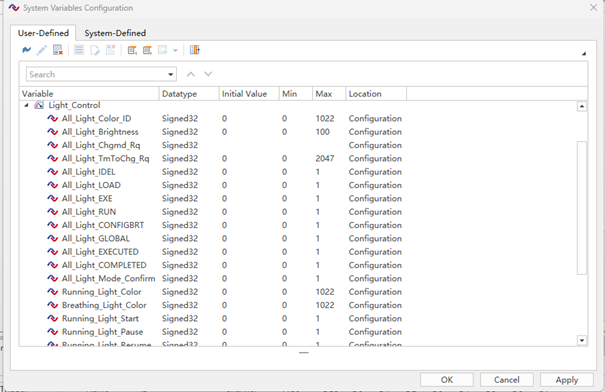
Add environment (system) variables
Similar to CAN, we can manually add system variables to bind panels, signals, and system variables. The following system variables are added this time:
Panel design
Here when we first understand the LIN signal for the interior light bar setting in the LDF database, it can be seen that there are several different models of IDEL/LOAD/EXE/RUN/GLOBAL/CONFIGBRT, and the dynamic effect of flow lamps and breathing lights can be realized through interaction.
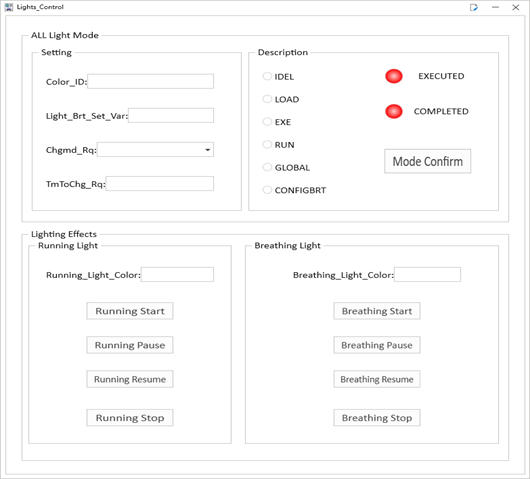
C applet implementation
In order to make the code have good readability and portability, try to process the single module program separately through .h/.cpp in the programming process to reduce the coupling between each other. Avoid problems such as duplicate definitions/function conflicts/data insecurity.
// All_Light_Control.h 包含所有关于Light_Control的功能函数声明
#ifndef __ALL_LIGT_CONTROL__H__
#define __ALL_LIGT_CONTROL__H__
void On_SysVar_All_Light_IDEL_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_LOAD_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_EXE_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_RUN_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_GLOBAL_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_CONFIGBRT_Mode();
void On_SysVar_All_Light_Mode_Confirm();
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Start();
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Pause();
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Resume();
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Stop();
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Start();
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Pause();
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Resume();
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Stop();
void On_running_light_timer(void *timer);
void On_running_light_control_timer(void *timer);
void On_running_light_global_timer(void *timer);
void On_breath_light_timer(void *timer);
void On_breath_light_control_timer(void *timer);
void On_breath_light_global_timer(void *timer);
void On_idle_mode_timer(void *timer);
void On_close_all_light_timer(void *timer);
void reset_current_radio_state(int var);
#endif
//common.h 包含所有需要用到的定义.h文件/枚举值/静态全局对象等
#ifndef __COMMON__H__
#define __COMMON__H__
#include "BaseMiniProgram.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "SystemVariableDefine.h"
#include "MainPanel.h"
#include "AutoAddress.h"
#include "Identfication.h"
#include "Temperature_Control.h"
#include "All_Light_Control.h"
typedef void* msTimer;
typedef struct message
{
int ID;
int DLC;
byte byte[8];
}message_t;
enum Setp_State{
WAIT_FOR_NEXT_STEPS = 0,
OPEN_EXTENDED_SESSION = 1,
RESET_LIGHT_BRIGHTNESS = 2,
CONFIGURE_LAMP_BOARD = 3,
CONTROL_ECU_POSITION = 4,
END_PROCESS = 5,
OPEN_EXTENDED_SESSION_FAILED = 6,
RESET_LIGHT_BRIGHTNESS_FAILED = 7,
CONFIGURE_LAMP_BOARD_FAILED = 8,
CONTROL_ECU_POSITION_FAILED = 9,
END_PROCESS_FAILED = 10,
CURRENT_STEP_PASSED = 11,
CURRENT_STEP_TIMEOUT = 12,
UDS_RESPONSE_SUCCESSED= 254,
UDS_RESPONSE_FAILED = 255,
};
enum T_For_Timer{
T_UDS_CMD_OUTPUT = 200,
T_Response_TIMEOUT = 10,
T_KT_TIMEOUT = 20,
T_AUTO_STEP = 100,
T_SEND_UDS = 20,
T_OUTPUT_MSG = 10,
T_TEMP_CONTROL_TIMEOUT = 100,
T_COMMON_CONTROL_TIMEOUT = 100,
T_LIGHT_CONTROL = 40,
T_BREATH_GLOBAL = 3000,
T_BREATH_GLOBAL_NEXT = 1000,
};
enum Light_Mode
{
IDEL = 0,
LOAD = 1,
EXE = 2,
RUN = 3,
GLOBAL = 4,
CONFIGBRT = 5
};
static int uds_cmd_send_flag,send_page,page,common_cmd_send_flag,out_put_line[13];
static byte temp[255];
static message linMsg,linMsgResp;
static int NodeSel_Rq = 0;
static int response_header_flag = 0,step_result = WAIT_FOR_NEXT_STEPS,data_len,data_len_temp=0,only_load_flag = 0;
static byte uds_cmd_list[13][8],common_cmd_list[12][8];
static char cmd_result_code[255];
static byte lin_send_message[15][8];
static int light_set_flag = 0;
static LIN::AILC_LIG_Rq_LIN_ST3 light_sts;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.Temperature_LM_1_10_Read temp_all_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.Temperature_LIG_ECU_Read temp_lig_ecu_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_1_Read temp_lm_1_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_2_Read temp_lm_2_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_3_Read temp_lm_3_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_4_Read temp_lm_4_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_5_Read temp_lm_5_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_6_Read temp_lm_6_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_7_Read temp_lm_7_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_8_Read temp_lm_8_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_9_Read temp_lm_9_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_LM_10_Read temp_lm_10_read;
// diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.GA_Temperature_per_channel_Read temp_per_channel_read;
// diagResponse LIG_MBEAM.Temperature_LM_1_10_Read temp_all_read_resp;
void reset_autoaddress_execute_setps();
void set_Progress_Bar();
void reset_output_line_for_temperature_uds_cmd();
void reset_output_line_for_common_uds_cmd();
void init_common_cmd_list();
void get_temperature_value(int data);
#endif
#include "../Config/common.h"
int color_iter,color_first,color_end;
msTimer running_light_timer;
msTimer running_light_control_timer;
msTimer running_light_global_timer;
msTimer breath_light_timer;
msTimer breath_light_control_timer;
msTimer breath_light_global_timer;
msTimer idle_mode_timer;
msTimer close_all_light_timer;
int interval_ts;
int interval_br,br_flag=0,down_up_flag = 0;
//diagRequest LIG_MBEAM.LIG_Variant_Coding_Read lig_varoding_read;
int NodeSel_Count = 0;
int mode_flag = 0; // 0 running light 1 breath light
int running_light_output_flag = 0;
int idel_flag = 0;
int LIG_TmToChg = 50;
int array_for_light_control_mode[6] = {1,0,0,0,0,0};
void On_SysVar_All_Light_IDEL_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control:: All_Light_IDEL == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(0);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_LOAD_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_LOAD == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(1);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_EXE_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_EXE == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(2);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_RUN_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_RUN == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(3);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_GLOBAL_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_GLOBAL == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(4);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_CONFIGBRT_Mode()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_CONFIGBRT == 1)
{
reset_current_radio_state(5);
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_All_Light_Mode_Confirm()
{
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Mode_Confirm == 1)
{
if (array_for_light_control_mode[0] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
else if (array_for_light_control_mode[1] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
only_load_flag = 1;
light_set_flag = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_light_setting_timer);
}
else if (array_for_light_control_mode[2] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = EXE;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
light_set_flag = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_light_setting_timer);
}
else if (array_for_light_control_mode[3] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = RUN;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
light_set_flag = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_light_setting_timer);
}
else if (array_for_light_control_mode[4] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = GLOBAL;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
else if (array_for_light_control_mode[5] == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Color_ID;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Brightness;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = CONFIGBRT;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
if (Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq < 4){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_Chgmd_Rq;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_ChgMd_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = Light_Control::All_Light_TmToChg_Rq;
light_set_flag = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_light_setting_timer);
}
Light_Control::All_Light_EXECUTED = 0;
Light_Control::All_Light_COMPLETED = 1;
}
}
// //running light
// on diagResponse LIG_MBEAM.LIG_Variant_Coding_Read
// {
// if (!this.IsPositiveResponse())
// {
// NodeSel_Count = 16;
// }
// else{
// NodeSel_Count = this.GetParameter("PLIG_vMAM_amount");
// color_iter = getSignal(AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3_LIG);
// //cancelTimer(running_light_timer);
// //cancelTimer(running_light_control_timer);
// //cancelTimer(running_light_global_timer);
// //cancelTimer(breath_light_timer);
// //cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
// //cancelTimer(breath_light_global_timer);
// //灭灯
// NodeSel_Rq = 1;
// color_iter = 1;
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = VtSig_AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3_LIG::LOAD;
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = 0;
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = 0;
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = 1;
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
// light_set_flag = 1;
// start_timer(,true,On_close_all_light_timer,T_KT_TIMEOUT);
// if(mode_flag == 0){
// color_end = Light_Control::Color_Num_Frist);
// start_timer(,true,On_running_light_timer,500);
// }
// else{
// light_sts.AILC_LIG_TmToChg_Rq_ST3 = LIG_TmToChg;
// color_end = Light_Control::Color_Num_End);
// start_timer(,true,On_breath_light_timer,500);
// }
// }
// }
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Start()
{
if(Light_Control::All_Light_Mode_Confirm == 1){
mode_flag = 0;
// lig_varoding_read.SendRequest();
}
}
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Pause()
{
if(Light_Control::Running_Light_Pause)
{
//cancelTimer(running_light_timer);
//cancelTimer(running_light_control_timer);
//cancelTimer(running_light_global_timer);
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
}
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Resume()
{
if(Light_Control::Running_Light_Resume)
{
if(NodeSel_Rq == 1)
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_timer);
else
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_control_timer);
}
}
void On_SysVar_Light_Mode_Stop()
{
if (Light_Control::Running_Light_Stop == 1){
color_iter = 0;
//cancelTimer(running_light_timer);
//cancelTimer(running_light_control_timer);
//cancelTimer(running_light_global_timer);
NodeSel_Rq = 0;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
}
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Start()
{
if(Light_Control::Breathing_Light_Start == 1){
mode_flag = 1;
// lig_varoding_read.SendRequest();
br_flag = 0;
}
}
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Pause()
{
if(Light_Control::Running_Light_Pause == 1){
//cancelTimer(breath_light_timer);
//cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
//cancelTimer(breath_light_global_timer);
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
}
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Resume()
{
if(Light_Control::Breathing_Light_Resume == 1){
if(NodeSel_Rq == 1)
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_breath_light_timer);
else
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_breath_light_control_timer);
}
}
void On_SysVar_Breath_Mode_Stop()
{
if(Light_Control::Breathing_Light_Stop == 1){
color_iter = 0;
//cancelTimer(breath_light_timer);
//cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
//cancelTimer(breath_light_global_timer);
NodeSel_Rq = 0;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
}
void On_running_light_timer(void *timer)
{
//if(color_iter >= 1 && color_iter <= color_end)
//{
//light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = color_iter;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = color_end;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT*2,true,On_running_light_control_timer);
//color_iter++;
//}
//else
//{
// color_iter = 1;
//start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_running_light_timer);
//}
}
void On_running_light_control_timer(void *timer)
{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
if (NodeSel_Rq <= NodeSel_Count){
if(running_light_output_flag)
{
if(NodeSel_Rq == 1){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Count;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq - 1;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = 0;
light_sts.Transmit();
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_control_timer);
running_light_output_flag = 0;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = 50;
light_sts.Transmit();
running_light_output_flag = 1;
if(NodeSel_Rq == NodeSel_Count)
{
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT*2,true,On_running_light_timer);
}
else{
NodeSel_Rq ++;
}
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_global_timer);
}
}
}
void On_running_light_global_timer(void *timer){
if(idel_flag == 0){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = GLOBAL;
light_sts.Transmit();
idel_flag = 1;
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_global_timer);
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
light_sts.Transmit();
idel_flag = 0;
start_timer(T_LIGHT_CONTROL,true,On_running_light_control_timer);
}
}
// breathing light
void On_breath_light_timer(void *timer){
//cancelTimer(breath_light_timer);
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = color_end;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT*3,true,On_breath_light_control_timer);
//global帧
start_timer(T_BREATH_GLOBAL,true,On_breath_light_global_timer);
/*if(color_iter >= 1 && color_iter <= color_end)
{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Color_Rq_ST3 = color_iter;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = 1;
NodeSel_Rq = 0;
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = VtSig_AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3_LIG::LOAD;
start_timer(,true,On_breath_light_control_timer,T_KT_TIMEOUT);
if(color_iter == color_end)
{
color_iter = 1;
}
else
{
if(br_flag)
color_iter++;
}
}
else
color_iter = 1;
start_timer(,true,On_breath_light_control_timer,T_KT_TIMEOUT*3);
//global帧
start_timer(,true,On_ breath_light_global_timer,T_BREATH_GLOBAL);*/
}
void On_breath_light_control_timer(void *timer){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
if (NodeSel_Rq <= NodeSel_Count){
if(br_flag) //brt -> 0
{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = 0;
}
else{ // brt -> 100
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Brt_Rq_ST3 = 100;
}
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
if(NodeSel_Rq == NodeSel_Count)
{
if (br_flag){
br_flag = 0;
//cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_breath_light_control_timer);
}
else{
br_flag = 1;
//cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_breath_light_global_timer);
}
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
}
else{
//cancelTimer(breath_light_control_timer);
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT*3,true,On_breath_light_control_timer);
NodeSel_Rq ++;
}
}
}
void On_breath_light_global_timer(void *timer){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = GLOBAL;
light_sts.Transmit();
idel_flag = 1;
//cancelTimer(breath_light_global_timer);
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT*3,true,On_idle_mode_timer);
}
void On_idle_mode_timer(void *timer){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = IDEL;
if(NodeSel_Rq<=NodeSel_Count){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
if(NodeSel_Rq == NodeSel_Count){
//cancelTimer(idle_mode_timer);
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
//cancelTimer(idle_mode_timer);
start_timer(T_BREATH_GLOBAL_NEXT,true,On_breath_light_timer);
}
else{
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_idle_mode_timer);
NodeSel_Rq++;
}
}
}
void On_close_all_light_timer(void *timer){
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = LOAD;
if(NodeSel_Rq<=16){
light_sts.Transmit();
if(NodeSel_Rq == 16){
//cancelTimer(close_all_light_timer);
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
//cancelTimer(close_all_light_timer);
light_sts.AILC_LIG_Oprtn_Rq_ST3 = GLOBAL;
light_sts.Transmit();
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
}
else{
light_sts.AILC_LIG_NodeSel_Rq = NodeSel_Rq;
light_sts.Transmit();
start_timer(T_KT_TIMEOUT,true,On_close_all_light_timer);
NodeSel_Rq++;
}
}
else
{
NodeSel_Rq = 1;
light_sts.Transmit();
}
}
void reset_current_radio_state(int var)
{
for (int iter=0;iter<6;iter++){
array_for_light_control_mode[iter] = 0;
}
array_for_light_control_mode[var] = 1;
Light_Control::All_Light_IDEL = array_for_light_control_mode[0];
Light_Control::All_Light_LOAD = array_for_light_control_mode[1];
Light_Control::All_Light_EXE = array_for_light_control_mode[2];
Light_Control::All_Light_RUN = array_for_light_control_mode[3];
Light_Control::All_Light_GLOBAL = array_for_light_control_mode[4];
Light_Control::All_Light_CONFIGBRT = array_for_light_control_mode[5];
}
Timeline Trace window and Logging
As with CAN simulation, Timeline Trace windows and logging are an integral part of the LIN simulation process. The specific operation is the same as the previous section.
Engineering operation test
After completing the above configuration, readers can connect the corresponding devices, run the project in ETStudio, and switch the control mode of the light bar in the car according to different needs to observe the corresponding functional effects. It can also display the function effect according to the preset running lamp and breathing lamp control buttons.
Expanding the topic – about network management
In order to adapt to the continuous updating and upgrading of the automotive system, meet the normal operation of more and more ECU units, and reduce the functional consumption of the battery, network management (NM) came into being. In particular, the ECU unit where the instrument/main unit/seat adjustment unit light does not turn off immediately after the vehicle engine is turned off, requires good and reasonable network management logic. Through network management, these ECUs can be systematically hibernated, wake-up, and suspended mechanisms to ensure reliable vehicle communication and reduce the dormant power consumption of the vehicle system.
OSEK (Open Systems and their Interfaces for the Electronics in Motor Vehicles) network management and AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) network management are two widely used network management modes.
OSEK network management can be divided into two types: direct management and indirect management. The direct management method requires each node on the network to have a unique identity and specific network management packets, and provides a negotiation mechanism to control all nodes in the network to sleep at the same time. The indirect management method is to passively detect the periodic application packets of nodes in the network, and if the messages are not received for a period of time, the nodes are considered to be offline hibernation.
AUTOSAR network management requires nodes participating in network management to have a unique identification number and specific network management messages, and specifies the network working status to ensure that the ECU on the vehicle can wake up and sleep together.